This article covers how assessments use scoring to analyze survey responses, detailing the scoring range, and outcome types, and assigning weightage to question responses for precise data analysis and reporting.
What is Scoring?
Scoring is a method used to measure the responses of survey participants, which enables the analysis of data collected from their answers. The scoring system used can vary depending on the type of survey being conducted and the goals of the survey. In general, scoring involves assigning numerical values or ratings to responses, which can then be analyzed to identify trends and patterns in the data.For example, in a Likert scale survey, participants may be asked to rate their level of agreement with a series of statements using a scale of 1 to 5, with 1 being "strongly disagree" and 5 being "strongly agree." The scores are then tallied up and analyzed to determine the overall level of agreement or disagreement with the statements.
Similarly, in a Net Promoter Score (NPS) survey, participants are asked to rate the likelihood that they would recommend a product or service to others on a scale of 0 to 10. The scores are then used to calculate an overall NPS score, which can be used to gauge customer loyalty and satisfaction.
Why is Scoring Important?
Scoring an assessment is important because it provides a structured and objective way to collect and analyze data from survey responses, allowing organizations to make data-driven decisions based on the feedback they receive from their customers or employees. By assigning numerical values or ratings to responses, organizations can identify trends and patterns in the data and make data-driven decisions based on the feedback they receive.
Scoring also allows organizations to compare responses across different questions and different groups of participants, providing insights into areas of strength and weakness. For example, if a company conducts a customer satisfaction survey and finds that customers consistently rate their customer service experience low, they can focus on improving their customer service training and processes to address the issue.
Moreover, scoring also helps in making a comparison with benchmarks set by other organizations, industry standards, or results from a survey done previously within an organization. This comparison can provide valuable insights into how an organization is performing relative to its competitors, the industry as a whole, or its past, allowing it to identify areas where it needs to improve.
Overall, scoring an assessment is an important step in the survey process as it provides a standardized and objective way to collect and analyze data, allowing organizations to make data-driven decisions and take action based on the feedback they receive.
How Metolius Makes Scoring Easy
Metolius makes scoring easy by doing the math for you! Once a scoring range has been selected and the question responses have been assigned numerical values, results are immediately available after a participant has submitted their responses.
See this article on how to set up an assessment for scoring.
The Three Components of Scoring in Metolius
1) Response Score Range
The response score range (Figure 1) refers to the set of possible scores that can be assigned to the responses provided to participants in an assessment. The scoring range can vary depending on the type of assessment being used and the goals and objectives of the survey and should be carefully selected to ensure that the data collected is relevant, useful, and actionable.
In the example mentioned above, a 5-point Likert scale survey has a scoring range from 1 to 5, with 1 representing "strongly disagree" and 5 representing "strongly agree." The response options are assigned a numerical value based on where they fall on the 1-5 scale.
In the Net Promoter Score (NPS) example, typically a 0 to 10 scoring range is used, with 0 representing "not at all likely" and 10 representing "extremely likely." In this case, the response options are assigned a numerical value based on where they fall on the 0-10 scale.
The scoring range used in an assessment is important because it helps to provide a standardized and objective way to collect and analyze data. By defining a clear scoring range at the outset of the assessment process, organizations can ensure that the data collected is consistent and comparable across different responses and participants.
When creating an assessment or using a template, the scoring range is selected in the General Assessment Settings section of the Create New Assessment page or the Review and Edit page respectively.
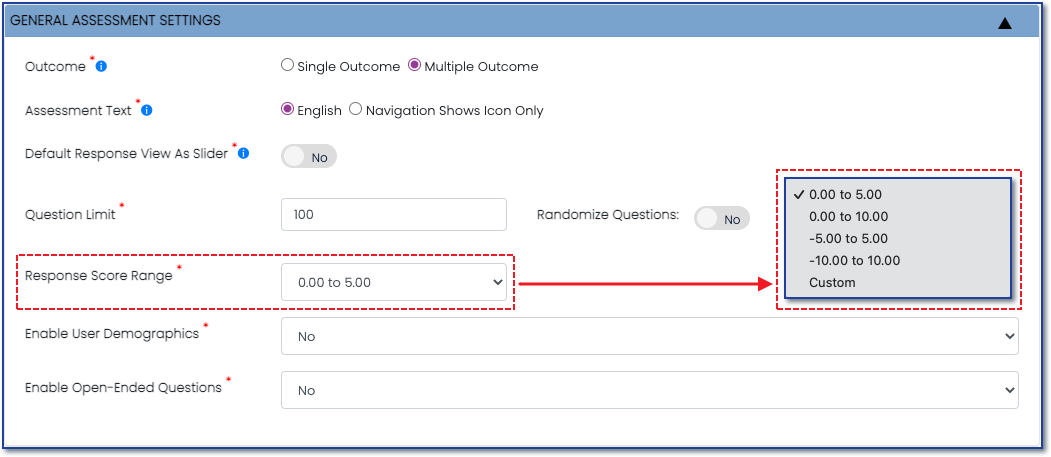 Figure 1
Figure 1 2) Outcome Type
Metolius offers two types of outcomes; One for data analysis, where the responses are scored, and another for Information Gathering where the responses are simply counted to offer statistical data. For more information, see this article on outcomes and this article on Assessments versus Surveys.
Scoring is only available in the Data Analytics Outcome type (Figure 2). When adding an outcome, choose the radio button next to Data Analytics. This outcome allows for assigning a numerical value to each of the Likert scale response options that you offer to the participants for answering the question.
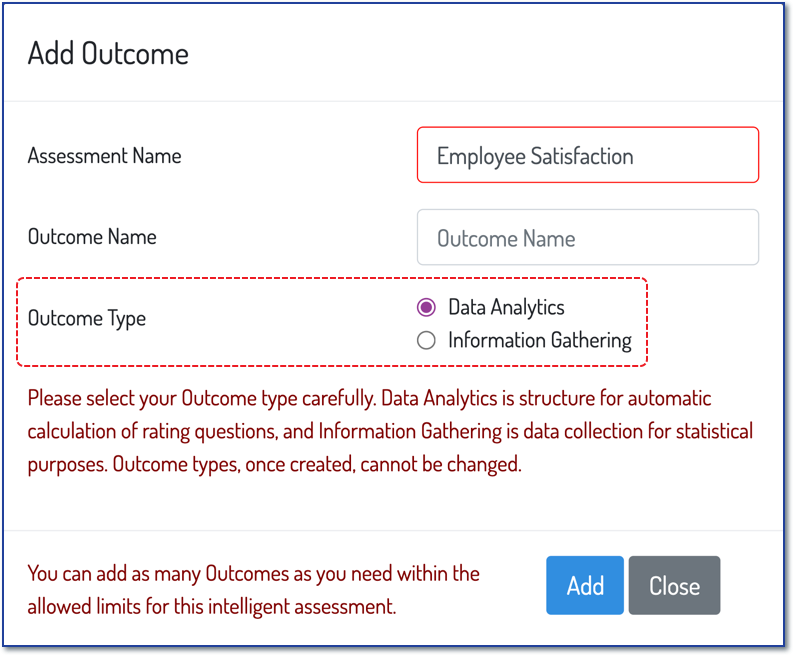 Figure 2
Figure 23) Question Response Weightage and Category
Response Weightage:
Response weightage assigns different values to the question response options. Values are assigned based on the importance or relevance of each response to the overall goals of the survey. In Figure 3, a value of 1-5 is assigned to each response option to align with the 5-point scale. Whichever option the participant chooses will be calculated into their score.
IMPORTANT
The weightage must align mathematically to the Response Score Range selected in the General Assessment Settings.
Response Category:
The response category column next to the weightage column adjusts how the score is calculated. See this article for more on Response Categories.
Positive - Choosing a positive response value will add a positive number to the score and affect the score positively; Effectively increasing the overall value.Neutral - Choosing a neutral response value neither adds nor subtracts a number from the score and the overall value is not affected.
Negative - Choosing a negative response value adds a zero to the score; Effectively reducing the overall value. Below is an advanced feature and most surveys do not need a negative
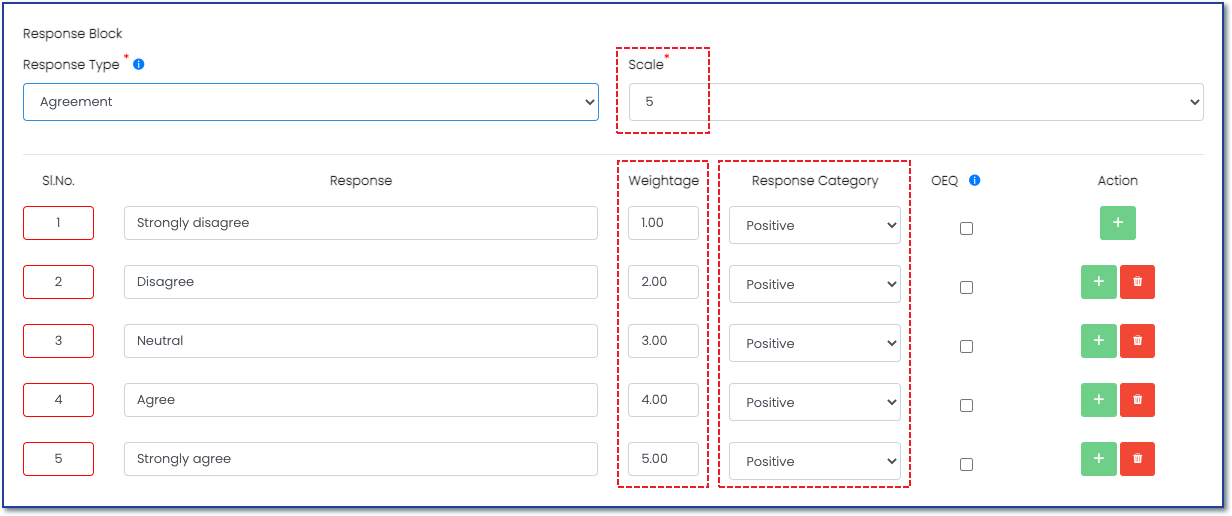 Figure 3
Figure 3
.png?height=120&name=Profile%20Blue(2).png)